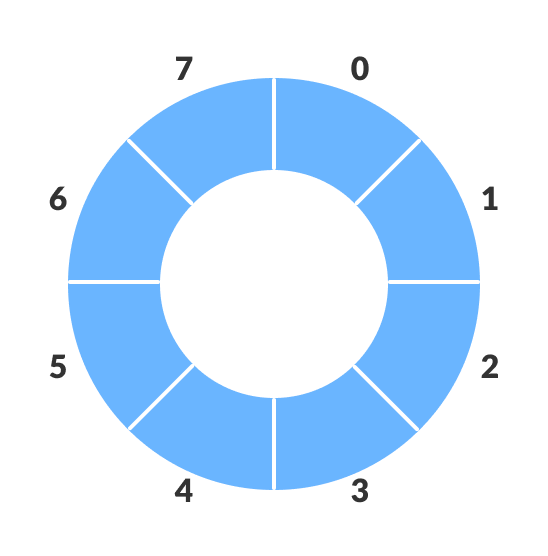
- Last element is connected to the first
- Specifically for In a normal queue, after a bit of insertion and deletion, there will be non-usable empty spaces at the start of the queue
- Implementing with linked list defeats the purpose of saving memory (using extra malloc)
Implementation
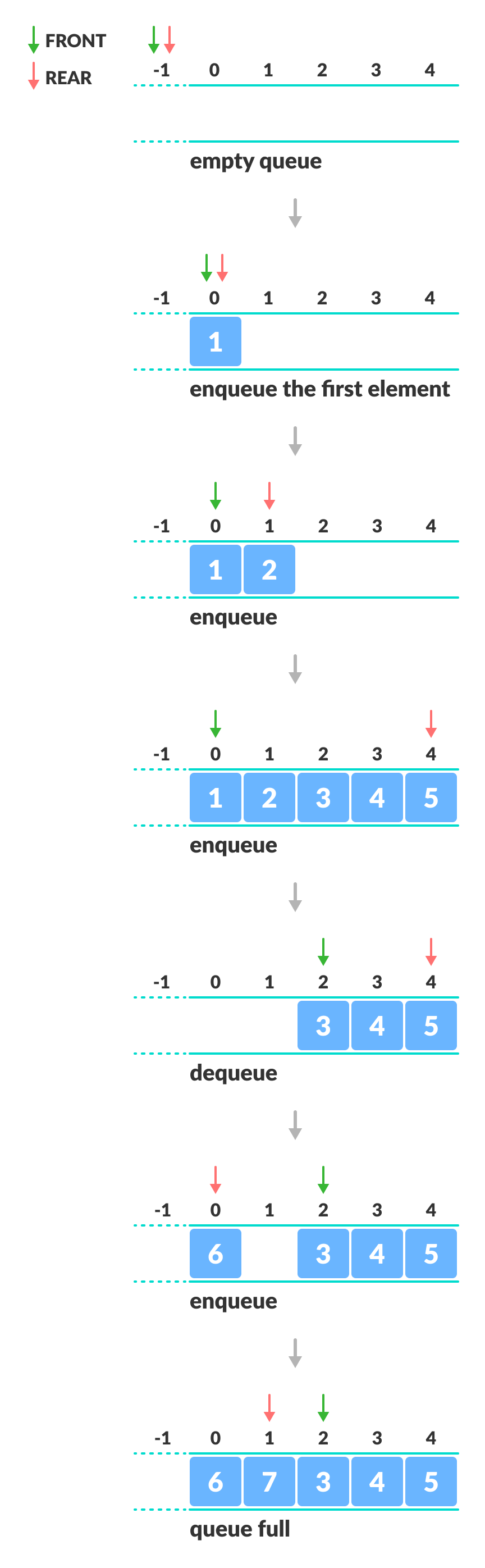
- Two pointers FRONT and REAR
- FRONT tracks first element of the queue
- REAR tracks last element of the queue (initialize both to -1)
class Circular_queue():
def __init__(self, k):
self.k = k
self.queue = [None] * k
self.head = self.tail = -1
def enqueue(self, x):
if (self.tail + 1) % self.k == self.head:
print('Circular queue is full')
return
if: self.head == -1:
self.head = 0
self.tail = 0
else:
self.tail = (self.tail + 1) % self.k
self.queue[self.tail] = x
def dequeue(self):
if self.head == -1:
print('Circular queue is empty')
return
if self.head == self.tail:
temp = self.queue[self.head]
self.head = -1
self.tail = -1
else:
temp = self.queue[self.head]
self.head = (self.head + 1) % self.k
return temp
def print(self):
if self.head == -1:
print('Circular queue is empty')
elif self.tail >= self.head:
for i in range(self.head, self.tail+1):
print(self.queue['i'], end = ' ')
else:
for i in range(self.head, self.k):
print(self.queue[i], end = ' ')
for i in range(self.tail+1):
print(self.queue[i], end = ' ')
example
Applications
- [[LC-622. Design Circular Queue]]
- [[LC-174. Dungeon Game]]