Fibonacci Heap
A fibonacci heap consists of a collection of trees which follow min heap or max heap property. In a fibonacci heap, a node can have more than two children or no children at all. The trees are constructed in a way such that a tree of order n has at least nodes in it, where is the Fibonacci number
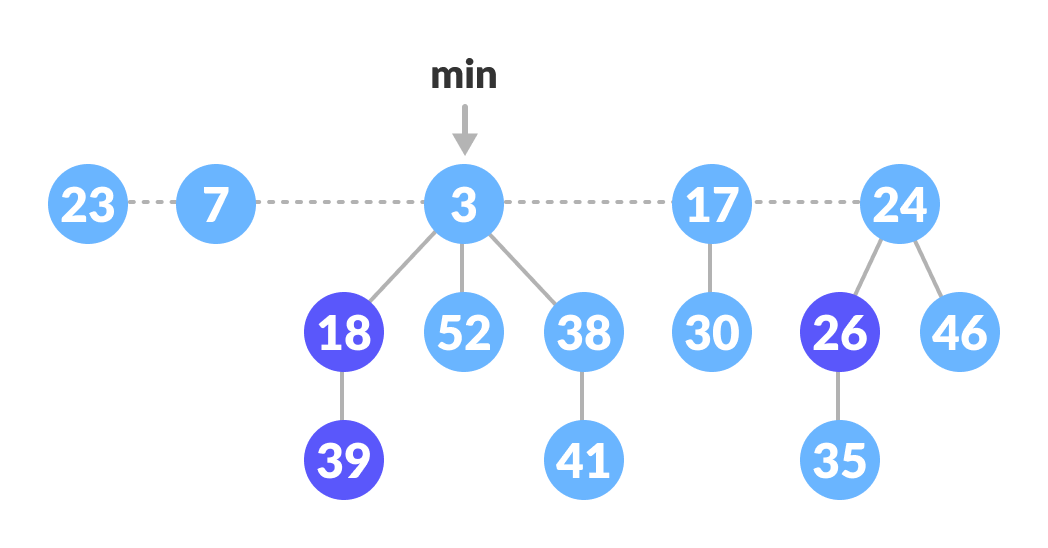
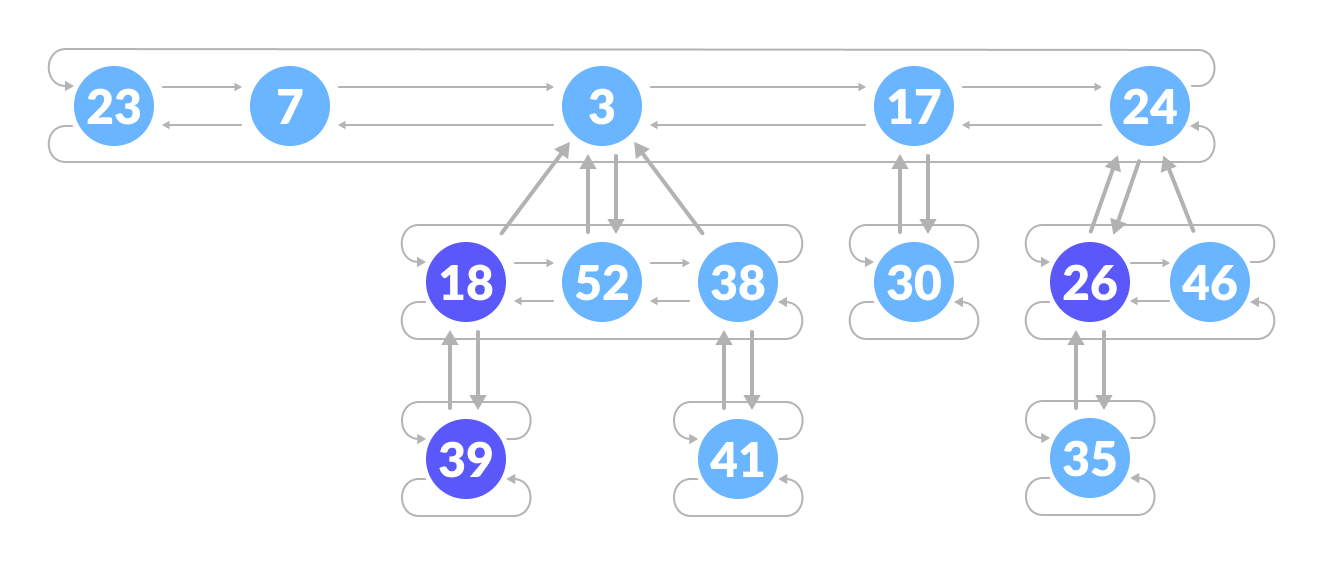
The roots of all the trees are linked together for faster access. The child nodes of a parent node are connected to each other through a circular doubly linked list. A circular doubly linked list is used because deleting a node from the tree takes O(1) time. The concatenation of two such lists takes O(1) time.
Properties of a Fibonacci Heap
- It is a set of min heap-ordered trees (I.e. the parent is always smaller than the children)
- A pointer is maintained at the minimum element node
- It consists of a set of marked nodes (Decrease key operation)
- The trees within a Fibonacci heap are unordered but rooted
Operations
Degree of node = # of children it has (not including grand children)
Extract Min
- Delete min node
- Set the min-pointer to the next root in the root list
- Create an array of size equal to the maximum degree of trees in the heap before deletion
- Repeate (steps 5-7) until there are no multiple roots with the same degree
- Map the degree of current root (min-pointer) to the degree in the array
- Map the degree of next root to the degree in array
- If there are more than two mappings for the same degree, then apply union operation to those roots such that the min-heap property is maintained
danger
To minimize the heights of trees after unions, we have to merge in a way such that the degree of the last tree is at most “max degree”. We should then merge trees with similar degrees which guarantees that the maximum degree will be the max degree pre-merge + 1
Max Degree
A binomial tree with degree d has nodes. A binomial tree with k nodes means the max degree is
Implementation
import math
class FibonacciTree:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.child = []
self.degree = 0
# Adding tree at the end of the tree
def add_at_end(self, t):
self.child.append(t)
self.degree += 1
class FibonacciHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.trees = []
self.least = None
self.count = 0
def insert_node(self, val):
new_tree = FibonacciTree(val)
self.trees.append(new_tree)
if self.least is None or val < self.least.value:
self.least = new_tree
self.count += 1
def get_min(self):
if self.least:
return self.least.value
return None
def extract_min(self):
smallest = self.least
if not smallest:
return None
for child in smallest.child:
self.trees.append(child)
self.trees.remove(smallest)
if self.trees == []:
self.least = None
else:
self.least = self.trees[0]
self.consolidate()
self.count -= 1
return smallest.value
def consolidate(self):
aux = (floor_log(self.count) + 1) * [None]
while self.trees:
x = self.trees[0]
order = x.order
self.trees.remove(x)
while aux[order]:
y = aux[order]
if x.value > y.value:
x, y = y, x
x.add_at_end(y)
aux[order] = None
order += 1
aux[order] = x
self.least = None
for k in aux:
if k:
self.trees.append(k)
if not self.least or k.value < self.value:
self.least = k
# Returns mantissa and exponent as a pair (m, e) value of a given number x.
def floor_log(x):
return math.frexp(x)[1] - 1
fibonacci_heap = FibonacciHeap()
fibonacci_heap.insert_node(7)
fibonacci_heap.insert_node(3)
fibonacci_heap.insert_node(17)
fibonacci_heap.insert_node(24)
print('the minimum value of the fibonacci heap: {}'.format(fibonacci_heap.get_min()))
print('the minimum value removed: {}'.format(fibonacci_heap.extract_min()))
Optimizations
Optimized Complexity
Time Complexity
| Operation | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Insertion | O(1) |
| Find Min | O(1) |
| Union | O(1) |
| Extract Min | O(logn) |
| Decrease Key | O(1) |
| Delet eNode | O(logn) |
Space Complexity
Related
Heap-Implementation Indexed-D-ary-Heap Indexed-Priority-Queue-(IPQ)